This guide shows how to manage environment variables in Windows, including how to edit, clear, and delete them.
Requirements
- Windows 7 or newer
- Administrative rights for some actions
What are Environment Variables?
Environment variables are key-value pairs that store configuration settings and can influence the behavior of software and operating systems.
In Windows, there are two types:
- System-Wide: These variables apply to all users and are typically to manage the operating system or shared applications.
- User-Specific: These variables are set per user and won’t impact other users on the same machine.
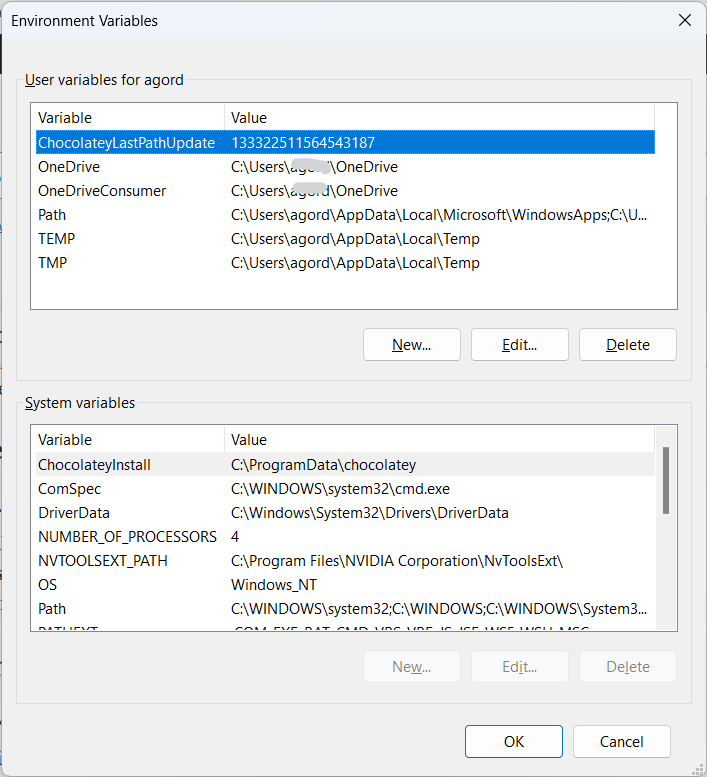
How to Edit Environment Variables
- Open the Start Menu: Simply press the
Windows key. - Search for Environment Variables: Type “Edit the system environment variables” and click on it.
- Access Environment Variables: Click the “Environment Variables” button in the new window.
- Edit or Add: You can either edit an existing variable or add a new one. Make your changes and click “OK”.
How to Delete Environment Variables
- Follow Steps 1-3 from above: This will get you to the list of environment variables.
- Select and Delete: Select the variable you wish to clear, and click the “Delete” button.
PowerShell Script for Automation
# Display current environment variables
Get-ChildItem Env:
# Remove a specific environment variable
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('VAR_NAME', $null, [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
Caution
- System Stability: Be cautious when editing or deleting system-wide environment variables as it can affect system stability.
- Administrative Rights: You’ll need administrative rights to modify some system-wide variables.